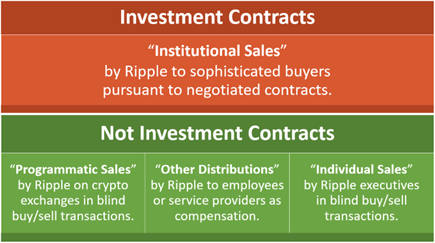
On July 13, 2023, the Federal District Court for the Southern District of New York issued the hotly anticipated ruling in the SEC’s case against Ripple Labs, Inc. (Ripple). On cross-motions for summary judgment, the court found that only Ripple’s sale of its XRP tokens to institutional buyers pursuant to sales contracts constituted unregistered sales of securities in violation of Section 5 of the Securities Act of 1933. But according to the court, Ripple’s programmatic sales of XRP through crypto exchanges, Ripple using XRP to pay employees and service providers and Ripple executives’ personal sales of XRP through exchanges are not investment contracts and therefore not sales of unregistered securities.
The court’s analysis focused on the Howey test for investment contracts, measuring each of the four types of XRP transactions at issue against the well-established factors for identifying a security. In a win for Ripple, the court did not waste time analyzing whether the XRP token itself was an investment contract and therefore a security. It stated that XRP “is not in and of itself a ‘contract, transaction[,] or scheme’ that embodies the Howey requirements of an investment contract.”
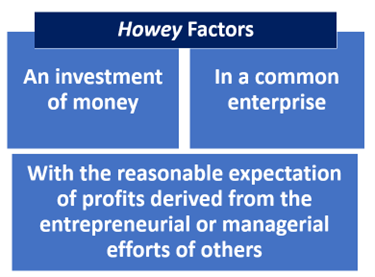
The court repeatedly emphasized the importance of evaluating the “economic reality” of the transaction at issue in order to appropriately apply the Howey standard. In the discussion regarding Ripple’s sales to institutional buyers, the court efficiently moved through its analysis that the first two Howey prongs were satisfied. In assessing whether the institutional buyers were purchasing the XRP for speculative motives, the court instructed that this should be an objective analysis of the promises and offers made to investors, not the specific reason for each individual investor’s decision.
The court points to Ripple’s marketing materials to institutional buyers that tied the success of Ripple overall to the success of XRP and its increase in value. Notably, Ripple’s marketing efforts highlighted that one of the value drivers for XRP is the talent of the Ripple team building the ecosystem around XRP. Combined with problematic public statements by Ripple executives that Ripple was committed to investing its capital in ways that would increase the price of XRP, the court found that the third Howey prong was satisfied.
The court bolstered this finding by analyzing the economic reality of the sales to institutional buyers, which were made pursuant to sales contracts that included lock-up provisions and resale restrictions. The court referenced similar facts from the 2020 ruling in the SEC’s case against Telegram, and concluded that, “[t]hese various provisions in the Institutional Sales contracts support the conclusion that the parties did not view the XRP sale as a sale of a commodity or a currency—they understood the sale of XRP to be an investment in Ripple’s efforts.”
“Of course, some Programmatic Buyers may have purchased XRP with the expectation of profits to be derived from Ripple’s efforts. However, ‘[t]he inquiry is an objective one focusing on the promises and offers made to investors; it is not a search for the precise motivation of each individual participant.’ Telegram, 448 F. Supp. 3d at 371”
In a victory for Ripple, the court held that Ripple’s sales of XRP through exchanges were not unregistered securities offerings. The court’s analysis focused only on the third Howey prong and found that because these sales were blind, bid/ask transactions facilitated through an exchange, the purchasers were ignorant to the fact that Ripple was the counterparty. As a result, there is no way to conclude that the purchasers knew they were contributing money to Ripple with the expectation that the proceeds from their purchase would be used to increase the value of XRP. The court noted that it is possible that some of these programmatic purchasers bought XRP for speculative purposes, but their individual motivation was not relevant. Again citing the Telegram decision, the court emphasized that Ripple could not have made promises or offers to these buyers because it had no idea who they were. The court engaged in a similar analysis in finding in favor of Ripple regarding its executives’ personal sales of XRP through exchanges.
In evaluating the other distributions of XRP by Ripple as payment for employees or service providers, the court concluded that the first Howey prong was not satisfied since there was no money exchanged. These recipients of XRP did not put up any capital that would be reinvested into the business by Ripple.
If it survives a potential appeal by the SEC, this decision can be seen as a win for Ripple and a blow to the SEC’s jurisdictional reach with respect to the regulation of digital assets, at least insofar as secondary market trading is concerned. Shortly after the opinion was released, XRP was reinstated on a variety of crypto exchanges for trading. Market participants should take note, however, that this ruling does not address secondary market sales of all digital assets on exchanges, but rather only held that Ripple’s sales and its executives’ sales of XRP through an exchange were not unregistered securities offerings under the Howey test. Because this case was being evaluated by the court as cross-motions for summary judgment, it only narrowly decided the issues of law in dispute. The court also held that Ripple had fair notice that its sales to institutional buyers could be illegal securities offerings based on advice it received from a law firm, and there were issues of fact that a jury will need to decide in order to determine whether Ripple executives aided and abetted this unregistered offering of XRP to institutional buyers.
- Partner
Mayme counsels clients on securities law matters, capital markets transactions, mergers and acquisitions and corporate governance issues. She is also a leader of the firm’s AI, Metaverse and Emerging Technologies practice and ...
The Hunton Andrews Kurth Blockchain Blog features opinions and legal analysis as we follow the development and use of distributed ledger technology known as the blockchain.
Search
Recent Posts
Categories
Tags
- 2019 Leaders’ Declaration
- 2020 National Strategy for Combating Terrorist and Other Illicit Financing (the 2020 Strategy)
- Advancing Innovation to Assist Law Enforcement Act
- Airdrops
- AML compliance program
- AML/CFT
- anonymity-enhanced cryptocurrencies
- Anti-Money Laundering
- Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2020 (AMLA)
- Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
- Antifraud
- Aon and Marsh
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Australia
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC)
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC)
- Automated Clearing House (ACH)
- Bank of England
- Bank Secrecy Act
- Bank Secrecy Act (BSA)
- Bank Term Fund Program
- Bermuda
- Biden Administration
- BIS
- Bitcoin
- Bitcoin Cash
- Bitfinex
- BitLicense
- Blockchain
- Blockchain Incubators
- Blockchain Legislation
- Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
- Blockchain Technology Act
- Brazil
- Breach of Contract
- Broker-Dealer
- Broker-Dealers
- BSA
- BSA Enforcement
- BTFP
- Bureau of Economic Analysis
- California
- Canada
- Captive Insurance
- CCPA
- Celebrity Endorsers
- Central Bank
- Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
- Centre for Information Policy Leadership (CIPL)
- CFTC
- Chapter 15
- China
- Christopher Giancarlo
- Civil Enforcement
- Class Actions
- Clearweb
- Colorado
- Commissioner
- Commodity Exchange Act
- Commodity Exchange Act (CEA)
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Complaint Bulletin
- Compliance
- Compliance Note
- Congress
- Connecticut
- Consent
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
- Consumer Protection
- Convertible Virtual Currency
- Corporate Compliance
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Transparency Act (CTA)
- Council of Institutional Investors
- Council of the European Union
- Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT)
- Covered Stablecoins
- Cross-Border Data Transfer
- crypto arbitrage trading accounts
- Crypto Assets
- crypto bank
- crypto custody
- Crypto Hackers
- Crypto Mining
- Crypto-commodity
- Crypto-currency
- Cryptoassets
- Cryptocurrency
- Cryptopia Limited
- Cryptosweep
- CVCs
- cybercrime
- Cybersecurity
- Dalia Blass
- DAO Report
- Darknet
- darknet marketplaces
- Data Privacy
- Data Protection Authority
- Davos
- decentralized finance (DeFi)
- DeFi
- Del. Michael San Nicolas
- Delaware
- Department of Business and Industry
- Department of Justice
- Department of Treasury
- DFS
- Digital Asset
- Digital Asset Securities
- Digital Assets
- Digital Commodities Consumer Protection Act of 2022
- digital currency
- digital currency ATM operators
- digital currency exchangers
- digital currency flows
- Digital Financial Assets Law (the Act)
- Digital Token Act
- digital token sales
- Digital Tokens
- Distributed Ledger
- Division of Corporation Finance
- Documentary Stamp Tax (DST)
- Dodd-Frank
- DOJ
- Economic Sanctions
- EDPB
- Eleventh Circuit
- Endorsement Guides
- Enforcement Action
- ePrivacy
- Ether
- Ether Classic
- EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- EU Regulation
- European Central Bank
- European Commission
- Exchange Act
- Exchange Traded Fund
- FDIC
- Federal Agencies
- Federal Election Commission
- Federal Reserve
- Federal Reserve Board
- Federal Trade Commission
- FedNow
- fiat currency MSBs
- Fiat-Backed
- Fight Illicit Networks and Detect Trafficking Act
- Figure Lending LLC
- Final Guidance
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
- Financial Privacy
- Financial Stability Board
- Financial Stability Oversight Council
- Financial Stability Report
- Financial Technology Protection Act
- FinCEN
- FINRA
- FinTech
- Florida
- Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
- Foreign Extortion Prevention Act (FEPA)
- Form 1099-DA
- Form BE-12
- fractional interests
- FTC
- Gemini Dollar
- Gemini Trust Company
- Global Consortium for Digital Currency Governance
- Group of Seven
- Group of Twenty (G20) Finance Ministers
- H.R. 5635
- Hard Fork
- Heath Tarbert
- Her Majesty’s Revenue & Customs (HMRC)
- HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC)
- home equity lines of credit (HELOCs)
- Homeland Security Assessment of Terrorists’ Use of Virtual Currencies Act
- House of Representatives
- House of Representatives’ Financial Services Committee
- Howey
- Howey test
- IEO
- iFinex Inc.
- Illinois
- India
- Information Sheet 225
- Initial Chain Offering
- initial exchange offerings (IEOs)
- Insurance
- Intellectual Property
- International
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Investor Protection
- IRS
- Jefferies Funding LLC
- Kenneth Blanco
- KYC/AML requirements
- Lael Brainard
- Large Platform Utility
- Legislation
- Legislature
- Liechtenstein Parliament
- liquidity
- Litecoin
- Litigation
- Louisiana
- Ltd.
- Malicious Cyber Activity
- Malicious Cyber Actor
- managed stablecoin
- Martin Act
- Maryland
- Metaverse
- model rule
- Monetary Policy
- Money Laundering
- Money Service Business
- money services businesses (MSBs)
- Mortgages
- Multi-Level Marketing Program (MLM)
- Mutual Fund
- Nakamoto
- narcotics
- NASAA
- Nebraska
- network maturity
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New York
- New York Attorney General
- New York Department of Financial Services (DFS)
- New Zealand
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token)
- NFTs
- Non-fungible tokens
- North Dakota
- North Korea
- NY Department of Financial Services
- OFAC
- Office of Investor Education and Advocacy
- Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Patent
- Paxos Standard
- Paxos Trust Company
- peer-to-peer exchangers
- Penalty
- Pennsylvania
- Personal Data
- Personal Information
- President Trump
- President’s Working Group (PWG)
- Privacy
- privacy coins
- Provenance.io
- Proxy Voting
- Public Blockchain
- rapid settlement
- real estate
- Regulation and Enforcement
- Rep. Sylvia Garcia
- Rescission
- Retail
- Ripple
- Ripple Labs
- Rule 233-1
- Russia
- Sanctions
- Sanctions Compliance Program (SHP)
- SAR lookback review
- SD8 coins
- SDN List
- SEC
- SEC crypto-securities
- SEC registration
- Securities
- Securities Act
- Securities Act of 1933
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Securities Exchange Commission
- security tokens
- Self-disclosure
- Senate Committee on Banking Housing and Urban Affairs
- Shareholder
- Shareholders
- SIFI
- Signature Bank
- Silicon Valley Bank
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Spencer Dinwiddie
- Stablecoins
- Stablecoins are Securities Act of 2019
- State-Sponsored Malicious Cyber Groups
- Suspicious Activity Report
- suspicious activity reporting (SARs)
- SVB
- SWIFT messaging system
- Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA)
- Switzerland
- synthetic hegemonic currency
- Taxation
- Templum
- Tennessee
- Terrorist Financing
- Tether Limited
- Texas
- Texas Business Organizations Code (TBOC)
- Texas Senate Bill 1859
- Texas Senate Bill 1971
- The World Bank
- three-year safe harbor
- Token and TT Service Provider Act
- token developers
- token transfer limits
- tokenization
- tokenized assets
- Trademark
- Travel Rule
- Trump Administration
- TT Identifier
- TT System
- TVTG
- U.S. Virtual Currency Market and Regulatory Competitiveness Act of 2019
- UCC Article 12
- UK Tax Rules
- unhosted wallets
- Uniform Commercial Code
- United Kingdom (UK)
- United Specialty Insurance Company
- United States Bankruptcy Code
- United States Patent and Trademark Office
- US central bank digital currency (US CBDC)
- US Department of the Treasury
- US Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC)
- US dollar
- US Treasury
- USTR
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Virtual Asset Service Providers
- Virtual currencies
- Virtual Currency
- Virtual Currency Consumer Protection Act of 2019
- Virtual Currency Exchange
- virtual currency license
- Virtual Currency Tax Fairness Act of 2020
- Virtual Markets Integrity Initiative
- Washington
- Weapons of Mass Destruction Proliferators Sanctions Regulations
- World Economic Forum
- Wyoming
- XRP
Authors
- Jimmy Bui
- Mayme Donohue
- Nicholas Drews
- Andrew Feiner
- Jason Feingertz
- Hannah Flint
- Katherine Gallagher
- Kevin E. Gaunt
- Armin Ghiam
- Carleton Goss
- Gregory G. Hesse
- Scott H. Kimpel
- Marysia Laskowski
- Michael S. Levine
- Lorelie S. Masters
- Patrick M. McDermott
- Uriel A. Mendieta
- Alex D. Pappas
- Daryl B. Robertson
- Natalia San Juan
- Caitlin A. Scipioni

